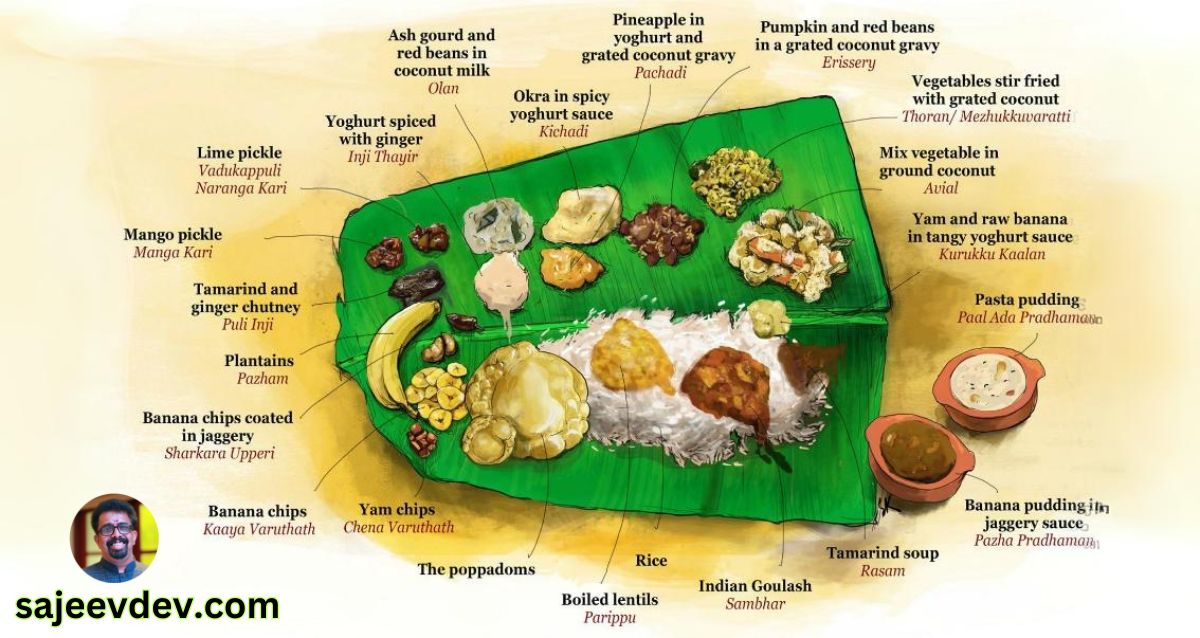
Onam Sadhya
Onam is one of the major festivals celebrated in the Indian state of Kerala, typically falling during the months of August or September. It marks the arrival of the harvest season and is a time of joy, unity, and cultural expression among Keralites. Celebrated with great fervor, Onam commemorates the legendary homecoming of King Mahabali, a figure symbolizing prosperity and equality. The festival spans over ten days, each filled with various cultural activities, traditional music, dance, and feasting.
Among the many traditions that characterize Onam, the Onam Sadhya holds a special place. This traditional vegetarian feast is served on a banana leaf and consists of a variety of dishes that reflect the rich culinary heritage of Kerala. The Sadhya is not merely a meal; it is a representation of the culture, hospitality, and agrarian lifestyle of the people. With approximately 26 to 30 dishes, Onam Sadhya includes rice, curries, pickles, and desserts, offering a unique blend of flavors that tantalize the taste buds.
A central philosophy of Onam Sadhya lies in its vegetarian nature, which reflects the region’s cultural value of Ahimsa, or non-violence. The feast showcases the use of local ingredients, emphasizing the connection to the land and nature. The variety of dishes in the Sadhya is also symbolic, as it represents the diversity of Kerala’s agricultural produce and culinary techniques. Overall, Onam Sadhya is not just a nutritional delight but also an embodiment of Kerala’s rich traditions and the harmonious existence of its people, celebrating both community and nature.
The Role of Banana Leaf in Onam Sadhya
Banana leaves hold significant cultural and nutritional value in Indian cuisine, particularly in the context of the traditional Onam Sadhya feast. Serving meals on banana leaves is a practice that goes beyond mere aesthetics; it is deeply rooted in health benefits and eco-friendliness. One of the primary advantages of using banana leaves lies in their natural properties, which enhance the flavor and nutritional profiles of the served dishes.
Scientifically, banana leaves are known to contain polyphenols, which possess antioxidant properties. These compounds can help neutralize free radicals in the body, thereby contributing to overall health and well-being. Additionally, the leaves have anti-bacterial properties, which can aid in food preservation and safety, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses during elaborate feasts like the Onam Sadhya. Such attributes make banana leaves an ideal choice for serving a variety of vegetarian dishes, which typically comprise the Sadhya.
Moreover, the act of serving food on banana leaves allows for a more connected and enriching dining experience. The texture and size of the leaves are adapted to accommodate an array of dishes, including rice, curries, and pickles, creating a visually stimulating meal presentation. The culinary experience is further enhanced by the natural aroma that the leaves impart to the food, engaging the sense of smell, which is integral to taste.
In addition to their health benefits, banana leaves are an environmentally sustainable option for serving food. These large leaves are biodegradable, minimizing waste compared to plastic or styrofoam alternatives. Thus, utilizing banana leaves aligns with sustainable dining practices, making them not only a traditional choice but also a modern, responsible one. The incorporation of banana leaves in the Onam Sadhya serves as a testament to the seamless blend of tradition, health, and ecological mindfulness.
Polyphenols: Immune Boosters from Banana Leaves
Banana leaves, traditionally utilized for serving the Onam Sadhya, are not only an aesthetic choice but also a repository of health benefits, primarily due to their high polyphenol content. Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds found in plants, renowned for their antioxidant properties. Interestingly, when hot food is placed on banana leaves, these polyphenols are released and absorbed into the food. This process enhances the nutritional value of the meal, making it not just a feast for the eyes but also for the body.
The immune-boosting properties of polyphenols are a key aspect of their importance in human health. Research has indicated that these compounds can help strengthen the immune system by modulating immune cell function and increasing the body’s resistance to infections. Additionally, polyphenols can reduce oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic diseases, including those affecting the immune system. By incorporating meals served on banana leaves into one’s diet, individuals may potentially enhance their immunity while enjoying a culturally significant gastronomic experience.
Beyond immune support, polyphenols in banana leaves exhibit antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. Studies have shown that these compounds can inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, making food safer to consume. This is especially significant for dishes served in traditional feasts like Onam Sadhya, where a variety of flavors and ingredients are combined. The natural barrier provided by banana leaves contributes to the overall hygiene of the meal, which is essential in communal settings. Thus, utilizing banana leaves is not merely a matter of tradition; it also aligns with a conscious effort towards improving health through natural means.
Antioxidants and Their Impact on Digestion
Banana leaves, traditionally used in the Onam Sadhya feast, contain a variety of antioxidants that play a significant role in promoting healthy digestion. These natural compounds help combat oxidative stress in the body, which is pivotal for maintaining overall wellness. In the context of digestion, antioxidants like phenolic acids and flavonoids present in banana leaves contribute positively by aiding in the facilitation of nutrient absorption and support of gut health.
The presence of antioxidants in banana leaves has been associated with a reduction in inflammation within the digestive tract. Inflammatory responses can hinder digestion and nutrient retention, often leading to gastrointestinal discomfort. By mitigating these effects, antioxidants assist in creating a more balanced environment in the gut, which is essential for optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients. Thus, utilizing banana leaves during meals, like in the Onam Sadhya, serves as more than just a cultural practice; it actively supports the digestive process.
Furthermore, incorporating meals served on banana leaves may enhance the bioavailability of nutrients due to the natural compounds found in the leaves. When food is placed on banana leaves, certain antioxidants are released into the food, thereby potentially increasing the nutritional intake of those consuming the meal. This dynamic interplay can lead to improved gut health, which is vital for both digestion and overall well-being. As consumers embrace traditional practices and foods like Onam Sadhya, they unknowingly partake in the beneficial properties that antioxidants offer through banana leaves.
Overall, the relationship between antioxidants found in banana leaves and healthy digestion cannot be understated. By advocating the consumption of such natural food presentations, individuals can harness these benefits, promoting better gut health and nutrient absorption.
Nutritional Balance of Onam Sadhya
The Onam Sadhya is renowned not only for its array of flavors but also for its impressive nutritional balance. This traditional feast, presented on a banana leaf, typically features an assortment of dishes that collectively provide a wholesome meal. At its core, Onam Sadhya comprises vital dietary components, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibers, vitamins, and minerals, harmoniously contributing to a balanced diet.
Carbohydrates constitute a significant portion of the Sadhya, primarily sourced from rice, a staple in most dishes. Rice provides energy through easily digestible carbs, making it an essential element of the meal. Additionally, several dishes incorporate lentils and legumes, which are rich in protein. These proteins are crucial for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily functions, enhancing the nutritional integrity of the feast.
Fats, though often viewed with skepticism, play an important role in the Onam Sadhya. Ingredients such as coconut and ghee not only add flavor but also provide essential fatty acids necessary for brain health and hormone production. Moderation is key, as these fats should complement the meal’s other components rather than dominate them.
Fibers, primarily found in vegetables like avial and sambar, aid in digestion and are integral to maintaining gut health. The wealth of vitamins and minerals present in the various vegetables used enriches the meal further, promoting immunity and overall wellness. The antioxidants from these plant-based ingredients assist in combating oxidative stress, which is essential for long-term health.
This diverse combination of nutrients inherent in Onam Sadhya creates a well-rounded meal that not only satisfies the palate but also nourishes the body, making it a perfect example of dietary balance in traditional cuisine.
Freshness of Locally Grown Ingredients
Onam Sadhya embodies the essence of using seasonal, locally sourced ingredients, which plays a significant role in creating this celebratory feast. The practice of sourcing ingredients from nearby farms not only enhances the flavor, but it also offers substantial nutritional benefits. Fresh produce, such as vegetables and fruits, contains higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants when consumed shortly after harvest. This is particularly important for the dishes served during Onam Sadhya, where the vibrant colors and diverse textures of ingredients contribute to both visual appeal and healthfulness.
The incorporation of lentils, often sourced from local farmers, in the various dishes of Onam Sadhya is essential for a balanced diet. Lentils are rich in protein and fiber, making them an excellent addition for maintaining sustained energy levels while promoting digestive health. Moreover, the use of fresh coconut and spices also adds a unique nutritional profile to the overall meal. Coconut provides healthy fats, while local spices enhance digestion and metabolism, reinforcing a tradition that values wellness alongside culinary enjoyment.
Moreover, the environmental impact of utilizing local ingredients deserves mention. By choosing to support local agriculture, the carbon footprint associated with transporting food over long distances is significantly reduced. This conscious choice not only contributes to sustainability but can also foster a sense of community as families and friends gather to enjoy traditional dishes prepared with love and care from what their region has to offer. Such practices ensure that Onam Sadhya remains a celebration of both our heritage and of the natural bounty surrounding us.
Plant-Based Proteins: A Rich Source
The Onam Sadhya is a vibrant representation of Kerala’s culinary heritage, characterized by its array of flavors, colors, and nutrients. Among the diverse offerings served on the traditional banana leaf, lentils and legumes emerge as standout components, delivering a significant supply of plant-based proteins. These nutritional powerhouses are key ingredients in many dishes of the Sadhya, contributing to both the taste and health benefits of this celebratory meal.
Plant-based proteins serve as an essential source of amino acids, which are critical for various bodily functions including muscle repair, immune system support, and hormone production. Unlike animal proteins, which can be high in saturated fats, lentils and legumes present a healthier alternative, rich in fiber and low in calories. This property makes them particularly beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight and promoting digestive health. Furthermore, they can be a crucial component of vegetarian and vegan diets, ensuring that individuals still receive adequate levels of protein without relying on animal products.
The nutritional profile of lentils and legumes extends beyond protein content; they are also abundant in vitamins and minerals such as iron, folate, and magnesium. These nutrients play vital roles in energy metabolism, blood production, and maintaining bone health. Moreover, incorporating lentils and legumes into meals has been associated with a host of health benefits, including reduced cholesterol levels, improved heart health, and a lower risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension.
During the Onam Sadhya, traditional dishes like Sambar and Thoran, which primarily feature lentils and various legumes, not only highlight the cultural significance of the feast but also underline the importance of including plant-based proteins in our diets. By embracing the nutritional wonders embedded in these simple yet effective ingredients, one can appreciate the scientific underpinnings of traditional Kerala cuisine.
Gluten-Free Delights of Onam Sadhya
Onam Sadhya, the lavish feast celebrated during the Onam festival in Kerala, is renowned for its vibrant array of dishes served on a banana leaf. A notable characteristic of many dishes in this traditional meal is their gluten-free nature. This ensures that individuals with gluten intolerance can partake in the celebration without health concerns, making it an inclusive culinary experience for all. The predominant ingredients used in Onam Sadhya, such as rice, lentils, and various vegetables, are naturally devoid of gluten, creating a wholesome assortment that caters to diverse dietary needs.
The health benefits of adhering to a gluten-free diet are increasingly recognized. For those with celiac disease, consumption of gluten can provoke severe health issues, including digestive disturbances and nutritional deficiencies. Furthermore, many individuals without celiac disease report improved digestion and reduced inflammation when removing gluten from their diet. As such, the gluten-free offerings in Onam Sadhya provide an excellent option for those seeking to avoid gluten while enjoying traditional Kerala cuisine.
Among the dishes served, items like ‘sambar’ (a lentil-based vegetable stew), ‘avial’ (a mixed vegetable curry), and ‘thoran’ (stir-fried vegetables with grated coconut) showcase the versatility and flavor of gluten-free cooking. Each of these dishes emphasizes the use of local produce and spices, thereby reflecting the rich agricultural bounty of Kerala. Additionally, desserts such as ‘payasam’ made from rice and coconut milk further enrich the gluten-free offerings of Onam Sadhya, ensuring that the feast concludes on a sweet note without compromising dietary preferences.
Ultimately, the gluten-free nature of most dishes served during Onam Sadhya celebrates inclusivity and health, allowing everyone to indulge in the festive spirit while enjoying nutritious and delicious food.
The After-Meal Tradition: Digestion with Betel Leaf
One of the significant cultural practices associated with the Onam Sadhya is the tradition of chewing betel leaf after the meal. This ritual encompasses the use of betel leaf, lime, and arecanut, which together create a traditional post-meal digestif. The consumption of this combination has been a longstanding custom in many Indian households, especially in Kerala, where Onam is celebrated with great enthusiasm. The act of chewing betel leaf has implications that extend beyond mere tradition; it integrates well with the overall nutritional structure of the Onam Sadhya.
Betel leaf, known for its aromatic properties, contains essential oils that are believed to stimulate digestive enzymes, thereby enhancing the process of digestion. The antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of betel leaves contribute to better gut health, making this a beneficial addition to the post-meal routine. Furthermore, the lime used in the mix is rich in vitamin C, which aids in the absorption of iron from the different curries served during the feast, thus promoting overall nutritional balance.
Arecanut, another component of the mix, is known to have stimulating effects that can help in alleviating mild digestive discomfort. While arecanut is often consumed in moderation, its role in this tradition highlights the cultural belief in natural remedies to support digestion. The combination of these elements reflects an understanding of food as not just sustenance but as part of a holistic approach to well-being.
In conclusion, the practice of chewing betel leaf post-Onam Sadhya encapsulates a unique blend of gastronomic and cultural elements that enhance the dining experience. This tradition not only acts as a digestive aid but also serves as a testament to the rich heritage of Kerala, emphasizing the importance of mindful eating and appreciating the symbiotic relationship between food and health.